Mac torrent download software. posted on September 13, 2018 under,. posted on December 12, 2018 under,.
There are still a few, however. Note that if you’ve got a multi-part set of.RAR files, you’ll want to extract the first file in the set—7-Zip will handle the other files in the set automatically.There are other Windows apps that support extracting RAR files, but we recommend 7-Zip because it’s open source, free, and reliable. Open a RAR File in macOSThere are not as many choices for opening RAR files on macOSX as on the more popular Windows platform. Rar opening free.
Sep 06, 2019 Task manager for Windows 7 Home. When I open task manager, all that comes up is the 'End Process' section. Even on Windows XP, I had the full task manager options, like: Applications,end process, performance. But on Win 7 Home, all I get is the 'end process' column. On my laptop I have Windows 7 Ultimate and I get the full Task Manager. To get classic Task Manager from Windows 7 back in Windows 10, you need to do the following things: Download the setup program for old Task Manager in Windows 10 from here: Old Task Manager for Windows 10; Simply run the installer. It looks like this: Follow the steps in the installer wizard. After it finishes, start the Task Manager. How to Open Task Manager Windows 7/8/10. 1.Shortcuts open the Task Manager: CTRL, SHIFT, and Esc. Simultaneously, press CTRL, SHIFT, and Esc to open the Task Manager. If you are one of the keyboard addicts, this is the most convenient way to open the latest Task Manager in Windows. Aug 09, 2015 To get classic Task Manager from Windows 7 back in Windows 10, you need to do the following things: Download the setup program for old Task Manager in Windows 10 from here: Old Task Manager for Windows 10; Simply run the installer. It looks like this: Follow the steps in the installer wizard. After it finishes, start the Task Manager. 2 To bring up the Task Manager directly in Windows Vista, Windows 7 & Windows 8, Windows 10, press CTRL+SHIFT+ESC instead. This is the Task Manager shortcut in Windows 10/8.
When you access the Task Manager in Microsoft Windows 7, it's very easy to overlook the new features and other changes until you take a closer look. If you're coming from Windows XP, you'll discover that there are many new and improved features. If you're coming from Windows Vista, you'll find a familiar user interface, which has been polished up a bit.
In this edition of the Windows Desktop Report, I'll investigate Windows 7's Task Manager and show you how to quickly reap the benefits of my detective work.
This blog post is also available in PDF format in a TechRepublic download.
Accessing Task Manager
There are several ways that you can access the Task Manager in Windows 7. Of course, you can right-click on the Taskbar and select Task Manager from the context menu or you can press [Ctrl]+[Shift]+[Esc].
However, you can also call up Task Manager by launching its executable file. To do so, just click the Start button, type taskmgr in the Start Search box, and press [Enter]. Now, if you press [Ctrl]+[Alt]+[Delete], you'll see a full-screen menu, as shown in Figure A, and can click Start Task Manager.Figure A
Pressing [Ctrl]+[Alt]+[Delete] will bring up a full-screen menu with an option to Start Task Manager.
Applications tab
When you access the Applications tab, as shown in Figure B, you'll discover that the Task Manager operates exactly the same as it does in XP and Vista. It allows you to determine the status of a task as well as end, switch, or create a new task.Figure B
The Applications tab operates exactly the same as it does in XP and Vista.
While we're looking at the Applications tab, take note of the column headers. When you click a particular column header to sort the list, you'll see a small arrow in the column header that not only alerts you to which column header has the current sort but also lets you know if the sort is ascending or descending -- the arrow points up if the sort is ascending and points down if the sort is descending. You'll find this column header feature throughout Windows 7, where applicable.
Processes tab
When you're troubleshooting Windows 7, you'll discover that the Processes tab provides you with very detailed information. For example, you'll notice the Description column, which identifies each process, as shown in Figure C.Figure C
The Description column can provide very useful information in a troubleshooting situation.
If you need even more information, just pull down the View menu and choose the Select Columns command to reveal the Select Process Page Columns dialog box, as shown in Figure D. You can then get more descriptive detail by selecting the Image Path Name or Command Line check boxes. The Image Path Name setting shows the full path to the file behind the running process, while the Command Line setting shows the full command line, including the parameters or switches used to launch the process.Figure D
You can get even more descriptive information by adding the Image Path Name and Command Line headers to the Processes tab.
Other useful information about a particular process can be gleaned by right-clicking on a process and selecting the Open File Location or Properties commands, as shown in Figure E. When you select the Open File Location, Windows Explorer opens the folder containing the file, and when you select Properties, it opens the file's standard Properties dialog box.Figure E
You can right-click on a process and select the Open File Location or Properties commands.
Services tab
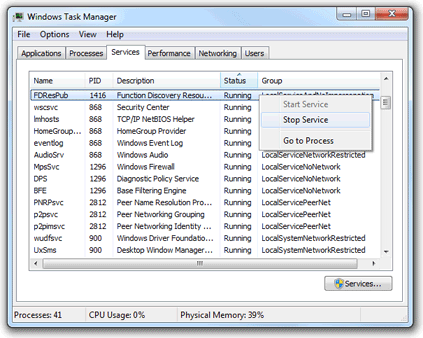
The Services tab, as shown in Figure F, provides you with a convenient way to quickly view the services that are running while you're troubleshooting.Figure F
The Services tab allows you to quickly assess the status of services on your system.
If you want to investigate whether a running service is tied to a particular process, you can right-click on the service name and select the Go to Process command, as shown in Figure G. When you do, Task Manager will then switch to the Processes tab and highlight the associated process.Figure G
Using the Go to Process tab makes it easy to identify services running as processes.
Keep in mind that if you click Go to Process and no process is highlighted in the Processes tab, the process may not be running under your user account. To view all processes, you'll need to click Show Processes from the All Users button.
If you need more control, just click the Services button to launch the full Services Microsoft Management Console.
Windows 7 Task Manager Not Showing Tabs
Performance tab
The most commonly accessed tab in Task Manager is the Performance tab, as shown in Figure H. If you're coming from XP, this is where you'll find the biggest changes. Let's take a closer look.Figure H
The Performance tab now provides information on actual memory usage.
In the Physical Memory section, the Total entry shows the amount of RAM installed in the system. The Cached entry indicates the amount of physical memory used recently for system resources. (This memory will remain in the cache in case the system resources are needed again, but it's available should other operations need it.) The new Available entry indicates the amount of physical memory that is currently not being used. The Free entry indicates the amount of memory being used in the cache but does not contain useful information.
The Kernel Memory section shows the amount of Paged and Nonpaged memory. The Paged and Nonpaged entries break down the total amount of memory being used by the kernel and show you how much of it is coming from virtual memory and how much is coming from physical memory, respectively.
In the System section, you'll find the Handles and Threads entries, which are actually sub-objects of processes. The Handles entry shows the number of object identifiers, or handles, that are currently in use by all running processes. The Threads entry actually refers to the number of sub-processes running inside of larger processes. The Processes entry, of course, represents the number of currently running processes. As you know, you can see each of the currently running processes by selecting the Processes tab.
Arduino book pdf download. The Up Time entry provides a nice piece of information that shows the amount of time that has passed since the computer has been restarted.

The Commit entry is a simple measurement that shows Page File usage. Here, the first number indicates the total amount of physical and virtual memory currently in use, while the second number indicates the total amount of physical and virtual memory available on your computer.
If you want more detailed performance information, you can click the Resource Monitor button. (I'll cover the Resource Monitor in more detail in a future blog post.)
Networking and Users tab
When you access the Networking and Users tabs, as shown in Figure I and Figure J, you'll see that they are essentially the same as in Windows XP. On the Networking tab, you can view network status and see how your network is functioning. On the Users tab, you can see who is logged on to the system.Windows 7 Task Manager Details
Figure I
The Networking tab displays a nice graph of the current network activity.
Figure J
The Users tab allows you to see who is connected or logged on to the system.
Windows 7 Task Manager Memory Explained
What's your take?
Windows 7 Task Manager No Tabs
Have you experimented with the Task Manager in Windows 7? What feature do you use the most? What feature would you like to learn more about? As always, if you have comments or information to share about this topic, please take a moment to drop by the TechRepublic Community Forums and let us hear from you.
Stay on top of the latest Microsoft Windows tips and tricks with TechRepublic's Windows Desktop newsletter, delivered every Monday and Thursday. Automatically sign up today!